Step 1
Perception of Threat
Stress begins with how we perceive potential threats, whether real or imagined. This initial assessment triggers the body's response system.

Stress isn't just a mental hurdle; it's a complex biological response that affects our entire body. Understanding how stress works can empower you to manage it more effectively. Here’s what you’ll discover about the biology of stress and its implications for your health.
Understanding the intricate biological response to stress is crucial for effective management. This visual illustrates the key components and interplay within your nervous system.
Stress begins with how we perceive potential threats, whether real or imagined. This initial assessment triggers the body's response system.
The SNS acts as the body's alarm, initiating the "fight-or-flight" response to prepare for immediate action.
Cortisol and adrenaline are released, increasing heart rate, enhancing alertness, and boosting energy levels.
Once the threat diminishes, the PNS works to restore balance, lowering heart rate and promoting relaxation.
When we think about stress, it often conjures images of overwhelming situations or anxious thoughts. But at its core, stress is a biological response deeply rooted in our physiology. As a clinical psychologist, I’ve seen firsthand how understanding this response can empower individuals to manage stress more effectively. Let’s dive into the basics together!
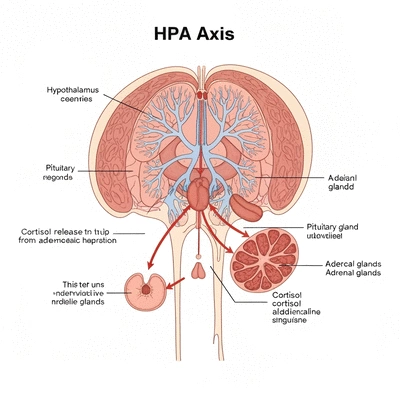
Stress is defined as the body’s reaction to perceived threats or challenges, triggering a complex interplay of biological mechanisms. These reactions are not just emotional; they have profound physical implications. Our bodies are designed to respond to stress, but when these responses become chronic, they can lead to serious health issues.
Stress can be simply defined as a state of mental or emotional strain resulting from adverse or demanding circumstances. Biologically, it activates our body’s stress response system, which prepares us to react quickly in challenging situations. Below are some key components of this response:
Understanding these elements can illuminate why stress feels so overwhelming. It’s not just a mental state; it’s a full-body experience!
The sympathetic nervous system (SNS) plays a pivotal role in how we respond to stress. Think of it as the body’s alarm system. When activated, it prepares the body for quick action. Here’s how it works:
This quick reaction is essential for survival, enabling us to navigate immediate threats. Yet, when stress becomes chronic, this response can lead to long-term health problems.
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates involuntary bodily functions and comprises two main branches: the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. While the SNS gears us up for action, the parasympathetic nervous system (PNS) is responsible for calming us down. Here’s what happens:
Recognizing the roles of both branches can help us develop strategies to better manage stress. It’s about fostering that balance in our daily lives!
Stress is not just a mental challenge; it manifests physically in the form of the fight-or-flight response. This intricate mechanism can have profound implications for our health.
We want to hear from you! What stress management technique do you find most effective?
Understanding the biological mechanisms behind stress is crucial for managing it effectively. The fight-or-flight response is an intricate process triggered by perceived threats, activating our body's survival instincts. This response, while beneficial in short bursts, can become detrimental when experienced chronically. By recognizing the symptoms of this response and its relationship with chronic stress, we can better equip ourselves for stress management.
Here are some key takeaways regarding the fight-or-flight response and the implications of chronic stress:
By internalizing these points, we can foster a better understanding of how our bodies react to stress and the importance of addressing it holistically.
At Stress Insight Solutions, we believe that knowledge is power. Empowering yourself against stress starts with education and awareness. If you're looking to delve deeper into this topic, several resources can provide further learning and support:

Utilizing these resources can significantly enhance your understanding and approach to stress management.
As you embark on your journey to manage stress, remember that what works for one person may not work for another. Tailoring your stress management strategies to fit your unique needs is essential! I encourage you to take the time to explore different methods and find what resonates with you. Whether it’s integrating mindfulness practices into your daily routine or finding time for physical activity, every small step counts.
The mind-body connection plays a significant role in how we experience and manage stress. It’s vital to recognize that our thoughts, emotions, and physical sensations are intertwined. For instance, practicing relaxation techniques not only calms the mind but also has physiological benefits, such as lowering heart rate and reducing cortisol levels. By nurturing this connection, we can enhance our resilience and overall well-being.
Ultimately, stress management is a personal journey. By acknowledging your stressors and actively engaging in coping strategies, you’ll be better equipped to lead a balanced life. Remember, at Stress Insight Solutions, we’re here to support you every step of the way!
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
We illuminate the causes and effects of stress through science-informed resources, empowering you to recognize stressors and implement effective coping strategies. Your mental well-being is our priority.
