HPA Axis Activation
The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis regulates stress hormones.
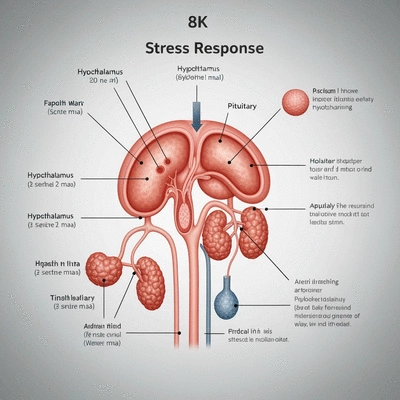
- 1 Hypothalamus (CRH)
- 2 Pituitary Gland (ACTH)
- 3 Adrenal Glands (Cortisol)

Stress isn't just a mental challenge; it's a biological one as well. Understanding the intricate systems that govern our stress responses can empower us to manage stress more effectively. Let's uncover the essential insights about the biological framework of stress!
An overview of the two primary systems, HPA Axis and SAM Axis, and their roles in the body's reaction to stress.
The Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis regulates stress hormones.
The Sympathetic-Adrenal-Medullary Axis triggers rapid fight-or-flight.
Regulates involuntary body functions in response to stress:
Chronic stress can lead to various issues:
Stress is a fascinating yet complex phenomenon that affects us all, and understanding its biological framework is crucial for managing it effectively. Our bodies have evolved intricate systems designed to respond to stressors, both physical and emotional. By grasping these mechanisms, we can better navigate the challenges that life throws our way. Let’s dive into the biological causes of stress and explore why they're important to understand!
When we talk about the biological causes of stress, we're looking at how our bodies react to various stressors. These can include anything from a looming deadline to a tough life event. Understanding these biological triggers helps us see that stress isn't merely a mental challenge; it's profoundly rooted in our physiology.
Biological causes of stress are tied to our body's responses to external and internal stimuli. Here are some key factors:
Understanding these biological causes can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their stress levels effectively. When we recognize how our bodies work, we can better equip ourselves to handle stress.
Exploring stress mechanisms isn't just an academic exercise—it's a practical approach that enables us to create effective stress management strategies. Here’s why this exploration matters:
At Stress Insight Solutions, we believe that education is a powerful tool for promoting mental well-being. By shedding light on these fascinating mechanisms, we aim to foster resilience and equip you with the knowledge to manage stress effectively!
Now that we've established the biological underpinnings of stress, let's explore how our bodies react to stressors through physiological systems. Understanding these systems is vital for effective stress management.
The two primary systems involved in the stress response are the HPA Axis and the SAM Axis. Each plays a unique role when our body perceives stress, working intricately to prepare us to handle challenges.
The hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) Axis is a key player in our body's stress response. Here’s how it works:
This activation of the HPA Axis illustrates the powerful connection between our brain and body during stressful situations. As cortisol levels rise, our body gears up for action, heightening our alertness. You can find more detailed information on the HPA axis and its role in stress response from this NCBI Bookshelf resource.
The interplay between these three components is crucial for understanding the stress response. The hypothalamus acts as a control center, while the pituitary gland serves as a messenger, guiding the adrenal glands to release cortisol. This trio effectively coordinates our response to stress, demonstrating how our body prepares itself for what lies ahead.
Alongside the HPA Axis, the sympathetic-adrenal-medullary (SAM) Axis is another key system involved in stress response. It works quickly to prepare us for immediate challenges.
Understanding the SAM Axis allows us to see how our body reacts swiftly to perceived threats, often leading to physical sensations like a racing heart or quickened breath. Recognizing these responses can help us develop strategies to manage them better.
The fight-or-flight response is a classic example of the body's immediate reaction to stress. This response is designed to protect us from danger, preparing us to either fight against a threat or escape. While this is essential in acute situations, chronic activation can lead to negative health outcomes. By becoming aware of this response, we can find ways to calm our systems and restore balance.
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) plays a crucial role in regulating our stress responses. It consists of two main branches: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system.
By understanding the balance between these two systems, we can implement techniques to enhance our parasympathetic response, thereby reducing overall stress levels!
The sympathetic response gears us up for action, while the parasympathetic response brings us back to a state of calm. Recognizing which state we’re in can empower us to choose coping strategies that help restore balance and resilience in our daily lives.
Here's a brief recap of the key points discussed so far:
As we dive deeper into the biological framework of stress, it’s vital to understand how our body reacts through various physiological mechanisms. These mechanisms can impact both our mental and physical health in profound ways. To recap, here's a brief overview of the key physiological responses and health impacts:
Understanding these biological causes of stress can empower us all to address our reactions effectively. With this knowledge, we can better navigate our daily lives and foster healthier responses to stressors.

At Stress Insight Solutions, we emphasize the importance of utilizing evidence-based strategies to manage stress. Recognizing the biological underpinnings is just the first step; we must implement practical solutions to mitigate these effects. This involves:
By implementing these approaches, we can not only address the biological aspects of stress but also improve our overall well-being. It’s all about creating a holistic strategy that fosters resilience and promotes mental health.
Now that we have explored the biological causes of stress, it’s time to turn knowledge into action! To leverage this understanding for better health:
Transforming knowledge into practice can lead to meaningful changes in your life. Remember, it’s about progress, not perfection!
I invite you to share your own experiences and the strategies you’ve found effective in managing stress. At Stress Insight Solutions, we’re building a community that values shared insights and collective growth. Whether you have a personal story or a unique coping mechanism, your input can inspire others!
Let's engage in a conversation about stress management. What techniques have worked for you? How do you navigate the challenges that life throws your way? Join in and let’s learn from each other’s journeys!
Here is a quick recap of the important points discussed in the article:
We illuminate the causes and effects of stress through science-informed resources, empowering you to recognize stressors and implement effective coping strategies. Your mental well-being is our priority.
